 |
The goal of
APMAC is to create remote sensing data sets at regional scale (104 - 105 km2) that directly constrain the methane emissions
for important source regions. The MethaneAIR and HALO instruments will be utilized on the G-III, and coincident observations by the MethaneSAT satellite, with repeated surveys of the
same region two-day periods, to create uniquely data-rich, comprehensive observations of methane concentrations and their changes over time that can fully constrain regional emission rates.
>> more |
|
 |
The overarching goal of
ARCSIX
is to quantify the contributions of surface properties, clouds, aerosol particles, and precipitation to the Arctic summer surface radiation budget and sea ice melt during the early melt season (May through mid-July).
It encompasses three main science questions and one objective:
>> more |
|
 |
The
ASIA-AQ
mission is an international cooperative field study designed to address local air quality challenges. Specifically, ASIA-AQ will contribute to
improving the integration of satellite observations with existing air quality ground monitoring and modeling efforts across Asia.
Satellite air quality observations are evolving with new capabilities from South Korea's Geostationary Environment Monitoring Spectrometer (GEMS). Traditional satellite
measurements from low earth orbit (LEO) are only available once per day. GEMS measures hourly to provide a new view of air quality conditions from space that both
complements and depends upon ground-based monitoring efforts of countries in its field of view.
>> more |
|
 |
PACE-PAX (2024)
The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem Postlaunch Airborne eXperiment field campaign is to support validation of the PACE mission. PACE-PAX will be conducted in September 2024, deploying two aircraft, each flying out of their home base.
>> more |
|
 |
FireSense
The NASA Science Mission Directorate (SMD) FireSense project is focused on delivering NASA's unique Earth science and technological capabilities to operational agencies, striving towards measurable improvement in US wildland fire management.
The NASA SMD FireSense project is part of a larger NASA wide Wildland Fire Initiative involving SMD, the Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate (ARMD), and the Space Technology Mission Directorate (STMD).
>> more |
|
 |
FASMEE
The Fire and Smoke Model Evaluation Experiment (FASMEE) is a multi-agency, interdisciplinary collaborative effort to identify and collect critical measurements of fuels, fire behavior, fire energy, meteorology, smoke, and fire effects that will be used
to evaluate and advance operational-used fire and smoke models. These data will promote science advancement that will give us a better understanding of wildland fire including how a fire behaves, the production and spread of smoke, and fire effects.
>> more |
|
 |
WHyMSIE (Westcoast & Heartland Hyperspectral Microwave Sensor Intensive Experiment) is the first step forward towards an integrated, intelligent,
and affordable PBL observing system of systems. It brings together multiple observing nodes - i.e., space, suborbital, and ground - from passive and active sensors to enable a comprehensive and coherent picture
of essential PBL thermodynamic variables such as temperature, water vapor, height, and hydrometeors to provide new understanding of the PBL that is not possible with any single sensor, observational approach, or scale.
>> more |
|
 |
The Balloon Network for stratospheric aerosol Observations (BalNeO) aims to provide key in situ measurements of stratospheric aerosols.
BalNeo brings together research laboratories from USA, Brazil, France and India to profile aerosol properties from the ground to the stratosphere. BalNeO is the heritage of a decade of balloon
deployments [2014-2025] across the world funded by the Upper Atmospheric Composition Observation program at NASA Langley.
>> more |
|
 |
TEMPO Validation Group
Launching in April, the Tropospheric Emissions: Monitoring of Pollution (TEMPO) instrument is the first mission capable of monitoring hourly air pollution over greater North America from a geostationary orbit of ~22,000 miles away. Routine products include nitrogen dioxide (NO2), formaldehyde (HCHO), and ozone with additional tropospheric composition products. To ensure the adoption of TEMPO data into research and decision-making activities to improve our understanding of air pollution, quantification of the accuracy and precision of these products is required.
>> more |
|
 |
SCOAPE
The Field phase of this experiment will be the SCOAPE Cruise in the Gulf of Mexico (GOM) to help NASA scientists evaluate how well air pollution can be monitored from space over coastal and open water. The SCOAPE Cruise will survey the GOM target area as a baseline prior to potential new growth. Research vessel instrumentation will include in situ surface pollutant monitors and a ship-based remote sensor (Pandora) that measures the atmospheric air similarly to satellite remote sensors.
>> more |
|
 |
STAQS (2023)
NASA's Tropospheric Emissions: Monitoring of POllution (TEMPO) mission is planned to launch in early 2023 to provide geostationary observations of air quality over North America.
With this addition of high-resolution satellite measurements, the Synergistic TEMPO Air Quality Science (STAQS) mission seeks to integrate TEMPO satellite observations with
traditional air quality monitoring to improve understanding of air quality science and increase societal benefit. STAQS will be conducted in summer 2023, targeting two primary
domains in Los Angeles and New York City and several secondary domains across North America with ground and airborne based measurements.
>> more |
|
 |
CPEX-CV
The NASA CPEX-CV field campaign will be based out of Cabo Verde during August-September 2022. The campaign is a continuation of CPEX – Aerosols and Winds (CPEX-AW), and will be conducted aboard the NASA DC-8 aircraft equipped with remote sensors and dropsonde-launch capability that will allow for the measurement of tropospheric aerosols, winds, temperature, water vapor, and precipitation.
>> more |
|
 |
ACCLIP
The Asian Summer Monsoon (ASM) is the largest meteorological pattern in the Northern Hemisphere (NH) summer season. Persistent convection and the large anticyclonic flow pattern in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere (UTLS) associated
with ASM leads to a significant enhancement in the UTLS of trace species from pollution and biomass burning origins...
>> more |
|
 |
CALIPSO-NVF
CALIPSO-NVF 2022 is a NASA airborne deployment of the LaRC HSRL-2 out of Bermuda for a series of nighttime underflights of the CALIPSO satellite. The goal is to verify the nighttime calibration and feature detection accuracy of the CALIPSO lidar.
|
|
 |
ACTIVATE
The overarching goal of ACTIVATE is to robustly characterize aerosol-cloud-meteorology interactions using extensive, systematic, and simultaneous in situ and remote sensing airborne measurements with two aircraft and a hierarchy of models. ACTIVATE focuses on marine boundary layer (MBL) clouds that span the continuum of stratiform and cumulus clouds and include post-frontal conditions. Together, these clouds cover more than 45% of the ocean surface and exert a large net cooling effect.
>> more |
|

|
DCOTSS
The main objective of DCOTSS is to investigate the impacts of intense thunderstorms over the U.S. on the summertime stratosphere.
During the summer, strong convective storms over North America overshoot the tropopause into the lower stratosphere. These storms carry water and pollutants from the troposphere into the normally very dry stratosphere, where they can have a significant impact on radiative and chemical processes, potentiallyincluding stratospheric ozone.
>> more |
|

|
SASA
The Student Airborne Science Activation (SaSa) program invites highly motivated early-career undergraduates (first- and second-year students) at eligible universities to participate in an 8-week summer research experience.
The SaSa program will draw on NASA SMD’s (Science Mission Directorate’s) unique assets (aircraft, aircraft sensors and experts) to create an effective learning environment, where students will take part in a paid summer internship for eight weeks (years 2-5). They will receive experiential learning experience delivered by NASA subject matter experts and guest lecturers, covering different topics such as basic remote sensing principles, basic atmospheric thermodynamics, atmospheric stability, and data analysis.
>> more |
|
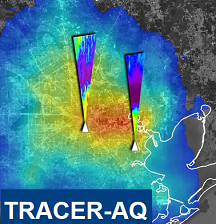 |
TRACER-AQ NASA will deploy assets to the Houston, Texas region to measure air quality relevant constituents at high spatial and temporal resolutions. This effort will be conducted in partnership with the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality, the Department of Energy (DOE)-led Tracking Aerosol Convection interactions ExpeRiment (TRACER) campaign, and a number of academic collaborators. This synergistic deployment approach aims to address research questions under the umbrella of three focus areas:
- Ozone Photochemistry and Meteorology
- Modeling and Satellite Evaluation
- Intersection of Air Quality and Socioeconomics Factors
>> more |
|
|
MOOSE
|
MOOSE
Southeast Michigan (SEMI) is currently designated as Nonattainment of the U.S. federal ozone standard and many locations in southern Ontario also frequently exceed the Canadian ambient air quality standard for ozone. The Michigan Department of Environment, Great Lakes, and Energy (EGLE) seeks potential attainment strategies for the SEMI area. EGLE and their partners at Ontario Ministry of Environment, Conservation and Parks (MECP), Environment and Climate Change Canada (ECCC), and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also want to better understand what contributes to elevated ozone levels in this Border region. To investigate, regulatory and scientific agencies including EGLE, MECP, the U.S. EPA, ECCC, NASA, and other partners, are conducting the Michigan-Ontario Ozone Source Experiment (MOOSE) in 2021 and 2022.
>> more |
|
 |
FIREX-AQ
The overarching objective of FIREX-AQ is to provide measurements of trace gas and aerosol emissions for wildfires and prescribed fires in great detail, relate them to fuel and fire conditions at the point of emission, characterize the conditions relating to plume rise, follow plumes downwind to understand chemical transformation and air quality impacts, and assess the efficacy of satellite detections for estimating the emissions from sampled fires.
>> more |
|
 |
CAMP²Ex
The Clouds, Aerosol and Monsoon Processes-Philippines Experiment (CAMP²Ex) is a NASA airborne mission scheduled for summer 2018 to characterize the role of anthropogenic and natural aerosol particles in modulating the frequency and amount of warm and mixed phase precipitation in the vicinity of the Philippines during the Southwest Monsoon. In partnership with Philippine research and operational weather communities, CAMP²Ex will provide a comprehensive 4-D observational view of the environment of the Philippines and its neighboring waters in terms of microphysical, hydrological, dynamical, thermodynamical and radiative properties of the environment, targeting the environment of shallow cumulus and cumulus congestus clouds.
>> more |
|
 |
OWLETS will use a unique combination of two ozone lidars, UAV equipped with O3 and surface sensors to characterize the water-land differences in O3.
-
One of the lidars(GSFC lidar) will be located in-land, while a second lidar(LaRC) will be located on the Chesapeake Bay Bridge Tunnel, 6-7 miles off-shore to obtain simultaneous “over-water” data.
-
UAV/drone with a in-situ O3sensor will allow us to investigate near-range vertical and horizontal gradients.
-
O3 sondes, fixed ground sensors, and mobile in-situ will also obtain measurements.
>> more |
|
 |
LISTOS
The Long Island Sound Tropospheric Ozone Study (LISTOS) is a multi-agency collaborative study focusing on Long Island Sound and the surrounding coastlines that continue to suffer from poor air quality exacerbated by land/water circulations. The goal of this study is to improve the understanding of ozone chemistry and transport from New York City and upwind regions to downwind areas, particularly over Long Island Sound.
>> more |
|
 |
The Atmospheric Carbon and Transport – America (ACT-America), will conduct five airborne campaigns across three regions in the eastern United States to study the transport of atmospheric carbon.
ACT-America will deploy two aircraft, a C-130 and UC-12, instrumented with remote and in situ sensors, to observe how mid-latitude weather systems interact with CO2 and CH4 sources and sinks to create atmospheric CO2/CH4 distributions.
>> more |
|
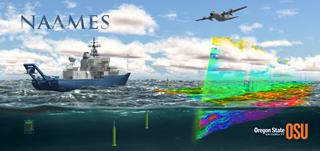 |
North Atlantic Aerosols and Marine Ecosystems Study (NAAMES) is an interdisciplinary investigation resolving key processes controlling marine ecosystems and aerosols that are essential to our understanding of Earth system function and future change. NAAMES is funded by the NASA Earth Venture Suborbital Program and is the first EV-S mission focused on studying the coupled ocean ecosystem and atmosphere.
>> more |
|
 |
ACEPOL
The Aerosol Characterization from Polarimeter and Lidar (ACEPOL) campaign will perform aerosol and cloud measurements over the USA from the NASA high altitude ER-2 aircraft using measurements from four spectro/photo polarimeters (RSP, AirMSPI, AirHARP, and AirSPEX) which differ in terms of spectral, angular, and spatial sampling. The measurements from these passive sensors will be complemented by measurements from active sensors (airborne HSRL-2 and CPL lidars).
>> more |
|
 |
LMOS campaign provides extensive observational air quality and meteorology datasets through a combination of airborne, ship, mobile lab, and fixed ground-based observational platforms. Additionally, chemical transport models (CTMs) and meteorological forecast tools assist in the planning for day-to-day measurement strategies. The main objectives of LMOS are to better understand the lakeshore ozone gradient and to evaluate and improve CTMs used for regulatory and research purposes in this region. LMOS 2017 is a collaborative effort between LADCO and its member states, NASA, NOAA, EPA, EPRI, Scientific Aviation, and a number of research groups at universities.
>> more |
|
 |
KORUS-AQ offers the opportunity to further advance NASA goals and those of its international partners related to air quality through a targeted field study focused on the South Korean peninsula and surrounding waters. The study
would integrate observations from aircraft, ground sites, and satellites with air quality models to understand the factors controlling air quality across urban, rural, and coastal interfaces.
>> more |
|

|
SARP: The Student Airborne Research Program (SARP) is a summer program for rising senior undergraduate students to acquire hands-on research experience in all aspects of a scientific campaign using NASA's airborne science laboratories for studying Earth system processes, calibration/validation of space-borne observations, and prototyping instruments for possible satellite missions. Participants will assist in the operation of instruments onboard the aircraft to sample atmospheric chemicals, and to image land and water surfaces in multiple spectral bands. Research areas include atmospheric chemistry, air quality, forest ecology, and ocean biology. Along with airborne data collection, students will participate in taking measurements at field sites.
>> more |
|
 |
The science objectives of ASCENDS are:
- to quantify global spatial distributions of atmospheric CO2 on scales of weather models in the 2010-2020 era
- to quantify the current global spatial distribution of terrestrial and oceanic sources and sinks of CO2 on 1-degree grids at weekly resolution
- and to provide a scientific basis for future projections of CO2 sources and sinks through data-driven enhancements of Earth system process modeling
|
|
 |
CARAFE:
- Assemble a versatile, economical system for measuring airborne fluxes
- Quantify greenhouse gas (GHG) sources/sinks over a spectrum of ecosystems
- Evaluate biophysical process models and parameterizations
- Validate top-level satellite flux products from OCO-2 and other missions
|
|
 |
DISCOVER-AQ: The overarching objective of the DISCOVER-AQ investigation is to improve the interpretation of satellite observations to diagnose near-surface conditions relating to air quality. To diagnose air quality conditions from space, reliable satellite information on aerosols and ozone precursors is needed for specific, highly correlated times and locations to be used in air quality models and compared to surface- and aircraft-based measurements. DISCOVER-AQ will provide an integrated dataset of airborne and surface observations relevant to the diagnosis of surface air quality conditions from space. >> more
>> DISCOVER-AQ Science |
|
 |
VIRGAS:
The objective of the Volcano-plume Investigation Readiness and Gas-phase and Aerosol Sulfur (VIRGAS) field experiment is to understand how natural and human-caused emissions of sulfur species, for example from volcanoes and from fossil-fuel power sources, ultimately influence climate, air quality, and visibility.
|
|
 |
ARISE: Acquire well calibrated datasets using aircraft and surface-basedsensors to support the use of NASA satellite and other assets for developing a quantitative process level understanding of the relationship between changes in Arctic ice and regional energy budgets as influenced by clouds.
>> more |
|
 |
SABOR:
The SABOR (Ship-Aircraft Bio-Optical Research) experiment, conducted in the summer of 2014 (July 17th to Aug 7th), brought together several teams to work on the issues of polarization of light in the ocean, focusing on several different scientific perspectives of this problem: biogeochemstry, radiative transfer, in situ, and remotely-sensed optics.
>> more |
|
 |
SEAC4RS: The SEAC4RS (Studies of Emissions and Atmospheric Composition, Clouds and Climate Coupling by Regional Surveys) Goals:
(1) To determine how pollutant emissions are redistributed via deep convection throughout the troposphere.
(2) To determine the evolution of gases and aerosols in deep convective outflow and the implications for UT/LS chemistry.
(3) To identify the influences and feedbacks of aerosol particles from anthropogenic pollution and biomass burning on meteorology and climate through changes in the atmospheric heat budget (i.e., semi-direct effect) or through microphysical changes in clouds (i.e., indirect effects).
(4) To serve as a calibration/validation test bed for future satellite instruments and missions.
>> more |
|
 |
DC3: The Deep Convective Clouds and Chemistry Project (DC3) field campaign investigates the impact of deep, midlatitude continental convective clouds, including their dynamical, physical, and lightning processes, on upper tropospheric (UT) composition and chemistry. The DC3 field campaign makes use of extensively instrumented aircraft platforms and ground-based observations. The NSF/NCAR Gulfstream-V (GV) aircraft is the primary platform to study the high altitude outflow of the storms, and is instrumented to measure a variety of gas-phase species, radiation, and cloud particle characteristics.
>> more |
|
 |
DEVOTE:The DEVOTE (Development and Evaluation of satellite ValidatiOn Tools by Experimenters) project will modify the NASA Langley B-200 aircraft to carry a suite of in situ instruments and then deploy this aircraft along with a remote sensor suite aboard the NASA Langley UC-12 aircraft to study aerosol and cloud optical and microphysical parameters.
|
|
 |
MACPEX: The Mid-latitude Airborne Cirrus Properties Experiment (MACPEX) is an airborne field campaign to investigate cirrus cloud properties and the processes that affect their impact on radiation. Utilizing the NASA WB-57 based at Ellington Field, TX, the campaign will take place in the March / April 2011 timeframe. Science flights will focus on central North America vicinity with an emphasis over the DoE ARM SGP site in Oklahoma.
>> more
|
|
 |
ARCTAS:The
Arctic is a beacon of global change. It is where warming has been
strongest over
the past century, accelerating over the past decades. It is an atmospheric
receptor of
pollution from the northern midlatitudes continents, as manifested in particular by thick
aerosol layers (“arctic haze”) and by accumulation of
persistent pollutants such as mercury.
>> View
ARCTAS White_Paper (2.6MB) |
|
 |
INTEX-B: The
first phase (INTEX-NA)
was completed in the summer of 2004 and the second phase, INTEX-Bfield
study, is to be performed during an approximate 8-week period from
March 1 to April 30, 2006...
>> View
INTEX-B White_Paper (1.0MB)
|
|
 |
INTEX-NA is to be performed in two phases. Phase A will take place
during the summer (July/August) of 2004 and Phase B during the spring (April/May)
of 2006. Phase A is in summer when photochemistry is most intense and climatic
issues involving aerosols and carbon cycle are most pressing, and Phase B
is in spring when Asian transport to North America is at its peak. Several
coastal and continental sites across North America have been selected as
bases of operation. The experiment will involve scientists from the US, UK,
Canada, Germany, and France, and will be supported by forecasts from meteorological
and chemical models, satellite observations, surface networks, and enhanced
O3-sonde releases.
|
|
 |
TRACE-P,
conducted in March/April 2001, had as it's major objectives to 1)
determine the chemical composition of the Asian outflow over the
western Pacific in spring in order to understand and quantify the
export of chemically and radiatively important gases and aerosols,
and their precursors, from the Asian continent and to 2) determine
the chemical evolution of the Asian outflow over the western Pacific
in spring and to understand the ensemble of processes that control
the evolution.
|
|
 |
GTE Field Campaigns (1983 - 2001) |
|